Press Processing
Press Processing
Yutaka has a system in place for mass production of stamped products with its own dies.
Yutaka can offer optimal process design with various thicknesses, materials, and production
systems, that incorporates CAE (analytical technique).

Technologies supporting stamping.
- Laminating press
- Self-manufacture of dies
- Precision processing
- Precision measurement
- CAE analysis
- Lamination manufacturing method
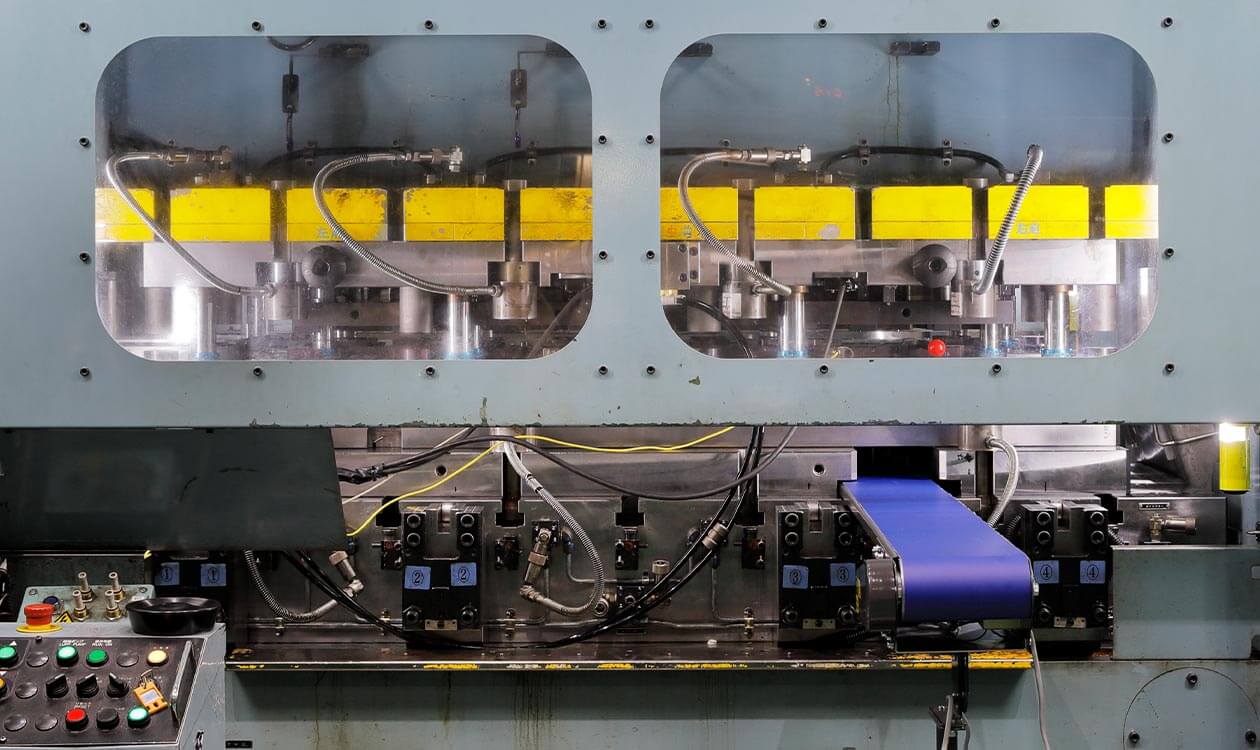
Laminating press
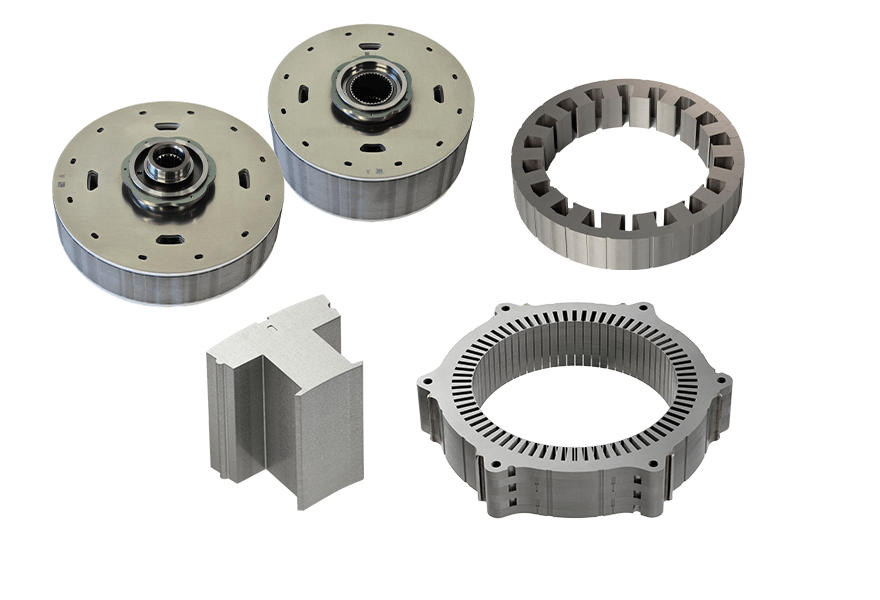
Yutaka has successfully produced T-core products based on one-point riveting lamination, which is its proprietary manufacturing process.
Yutaka also produces rotor and stator cores through composite lamination production with high-precision, high-speed large presses.
With production being supported by maintenance equipment such as large precision surface grinding machines and ultrasonic washing machines, Yutaka has established a maintenance method by which everything is completed within.
The introduction of a new TRY press has enabled the following advantages: trial runs equivalent to mass production and the timely launch of mass production.
Equipment

Introduction of low-cost equipment
Enhanced with UG expertise to achieve processing performance comparable to Japanese-made presses.
TRY Press MCP-400
Bolster size 3700×1200
-

MSP-4000
Bolster size 3360×1200 -

MSP-2200
Bolster size 2000×1000 -

Large precision surface grinding machine
-

Ultrasonic washing machine
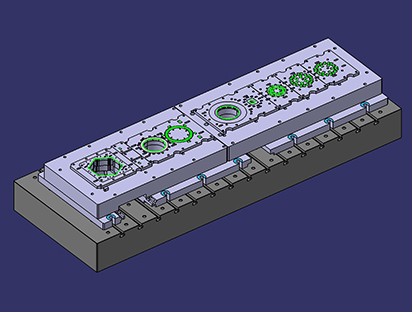
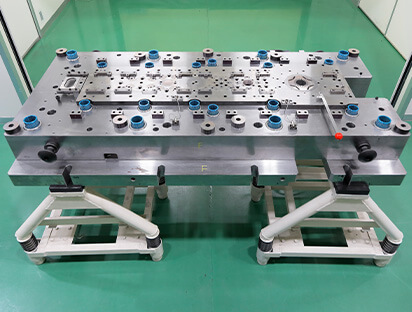
Self-manufacture of dies
Yutaka now manufactures its own laminating dies, which includes the processes of Planning and design → Production → Assembly and Try.
Yutaka is working hard to enhance its technical capabilities and competitiveness through
enhancement of its ability to come up with ideas for new manufacturing processes and new
structures and proposal of low-cost manufacturing processes.
Why does Yutaka manufacture its own dies?
Yutaka’s ownership is evidence of continual technical capabilities.
Enhancing new manufacturing processes, and new structures, and offering VA proposals
Establishing a global backup framework
Maintaining and managing stable mass production and implementing improvement measures completely on its own
Low-cost dies
Embodying its cost reduction concept and strengthening its ability to work with manufacturers
Human resource development
Early training and education based on “genba” (actual place), “genbutsu” (actual thing) and “genjitsu” (actual situation)
Equipment
-
CAE/die design
-
Precision processing
-

Adjustment/measurement
-

Trial/mass production
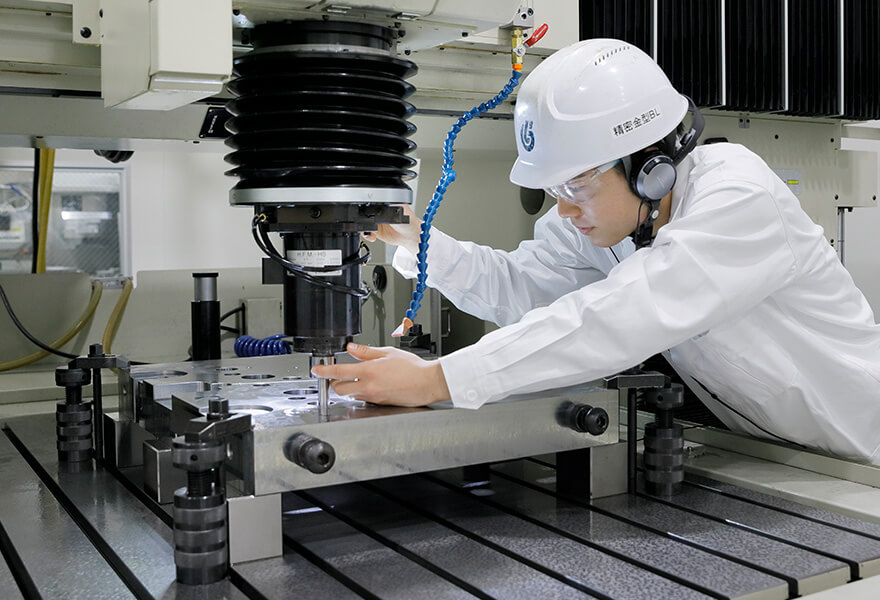
Precision processing
Yutaka's large processing machines enable us to processing large parts precisely (±2
μm). Processable range 1,580 mm × 1,020 mm
Yutaka has achieved a processing precision of ±1 μm through ultra-high precision
processing with wire-discharge processing machines.
High-precision processing has been achieved through the accumulation of processing
knowhow by experienced operators.

Equipment
-

Maximum processable range: X1,580 mm Y1,020 mm
Processing precision: ±2 μm
Temperature control: 23°C±1°C -

High-precision die parts processing (punch die)
Temperature control: 23°C±1°C -

Maximum processable range: X800 mm Y600 mm (water type)
Processing precision: ±2 μm
Temperature control: 23°C±1°C -

Chuck dimensions: X800 mm Y400 mm
Processing precision: ±2 μm
Temperature control: 23°C±1°C
Precision measurement
With the experienced operator’s measurement precision of ±1 μm, micron-precision
three-dimensional measurement is possible.
The temperature and humidity are controlled at 20°C±1°C and 50%±10%, offering a good
measurement environment.
Extremely small styluses with a minimum diameter of 30 μm have enabled touch
measurement of extremely small shapes, thereby enabling measurement of extremely
small radiuses.

Equipment
-

Mitsutoyo
Coordinate measuring machineMeasurement range:
X-axis 900 ㎜
Y-axis 1000 ㎜
Z-axis 600 ㎜
Maximum workpiece height:
850 ㎜ -

Mitsutoyo
Quick Vision -

Mitsutoyo
Contour tracer -

Constant-temperature chamber
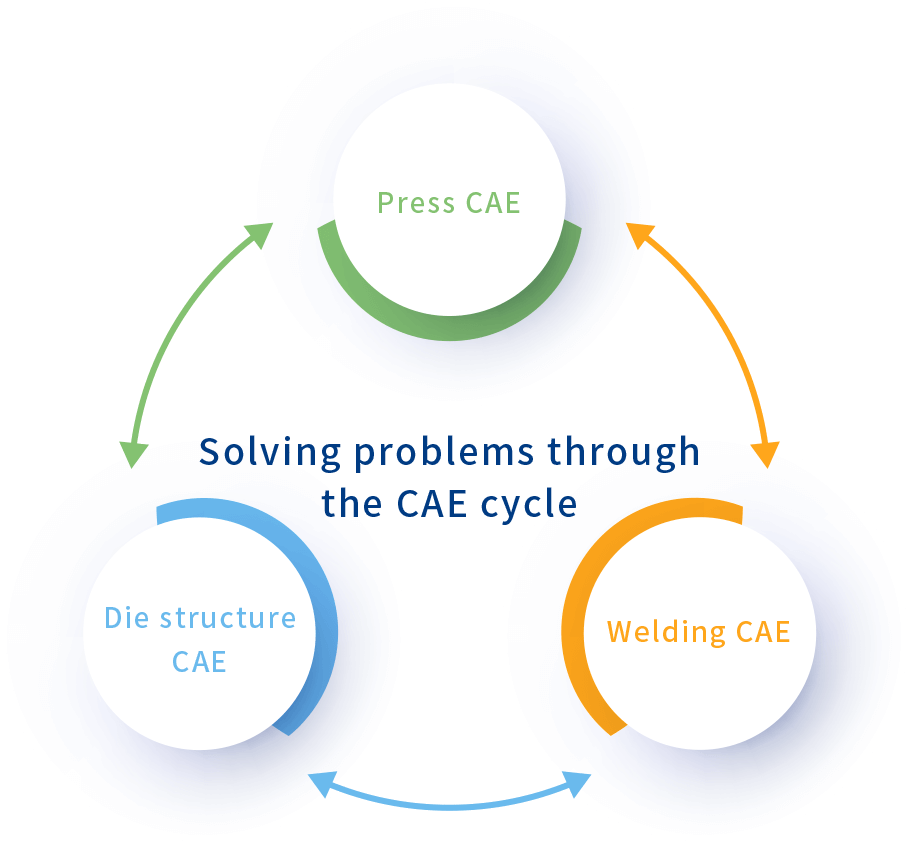
CAE analysis
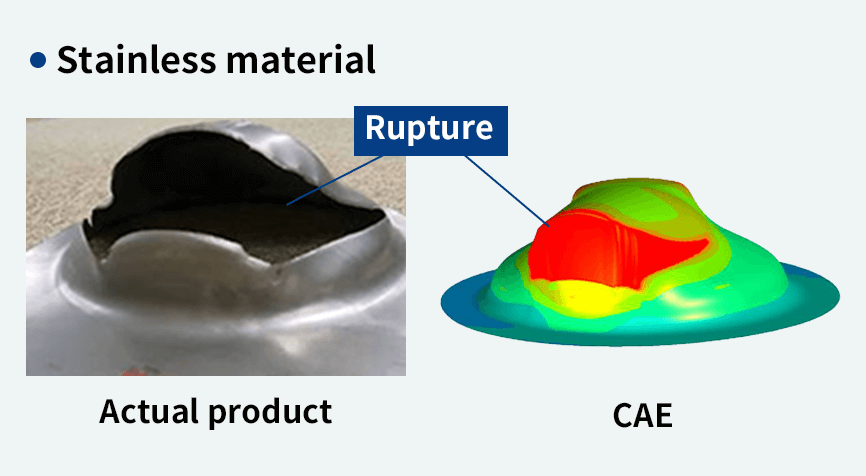
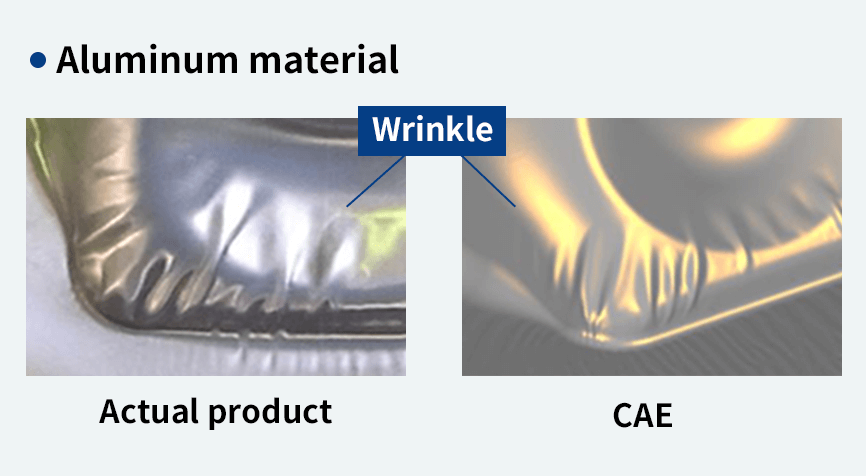
Through die process design, and press CAE, it is possible to analyze product
wrinkles, cracks, and spring back in plate stamping.
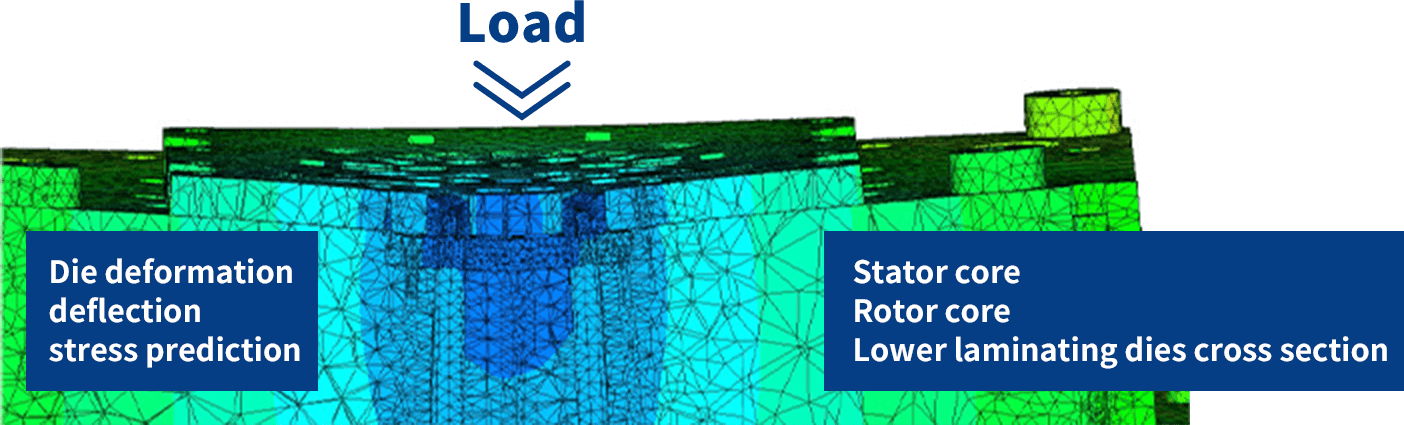
Through die design with die structure CAE, it is possible to analyze die
deformation, deflection, and stress.
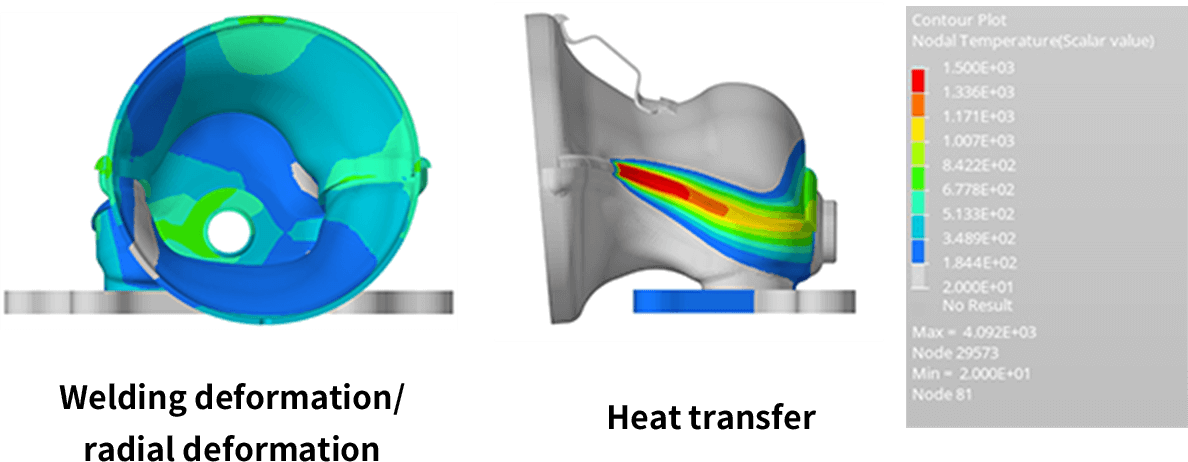
By reflecting product shapes obtained by welding CAE in dies, it is possible to
analyze thermal distortion, heat transfer, and temperature distribution after
product welding.
CAE
Press CAE
Offers accurate simulation without
differences from the actual equipment
Die structure CAE
Welding CAE
Lamination manufacturing method
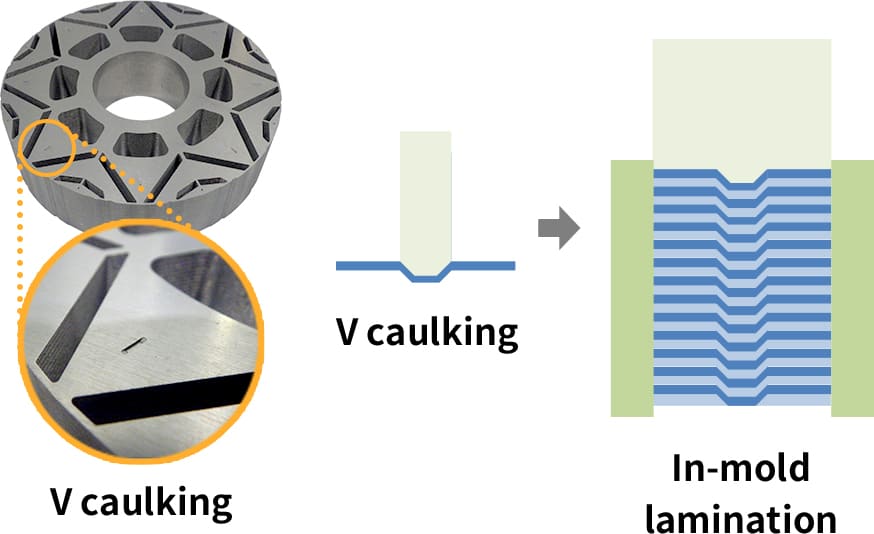
V caulking method
By prototyping and evaluating several types of V caulking shapes, we achieve the V caulking method that is optimal for a given product.
By forming V caulking, it is possible to secure sufficient caulking strength and mass-produce the product in a stable manner.
We have succeeded in laminating particularly thin sheets(t=0.2) out of the types of electromagnetic steel sheets.
Adhesion lamination method
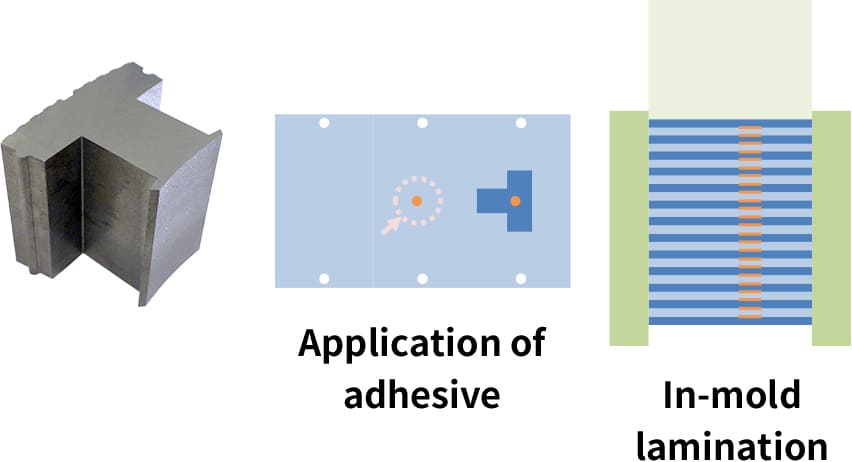
With our proprietary adhesion mechanism for bonding between laminated sheets equipped inside a mold, we have established the adhesion lamination method.
Compared to caulking and welding, the adhesive lamination suppresses iron loss and improves the motor efficiency.
Sites in Japan
Overseas Sites

If you have any orders or inquiries


